Arduino drone V2.0 - Acc raw data read
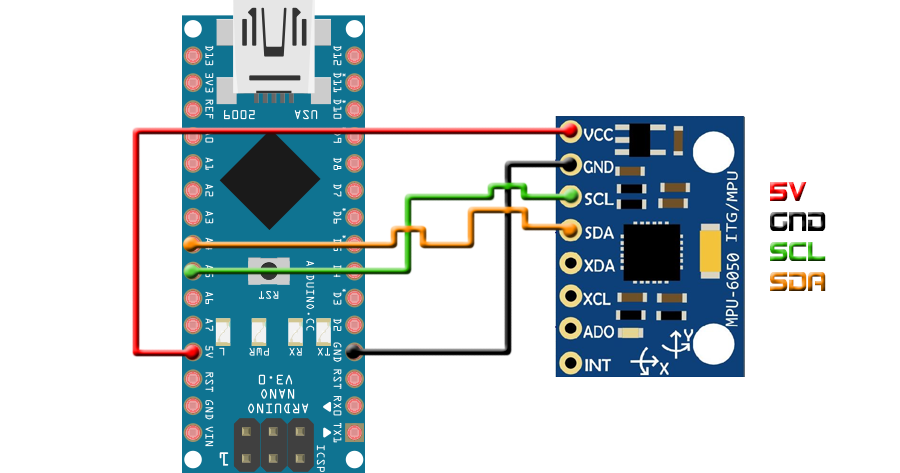
Unzip the file. Open the .ino file and upload it to the Arduino UNO/NANO. Make THIS connection open the serial monitor once uploaded. Remember to select 9600 baud rate or change the speed in the code.
Go back:
Or copy this code:
/* http://www.youtube.com/c/electronoobs
*
* This is an example where we configure te data of the MPU6050
* and read the Acceleration data and print it to the serial monitor
*
* Arduino pin | MPU6050
* 5V | Vcc
* GND | GND
* A4 | SDA
* A5 | SCL
*/
//Includes
#include <Wire.h>
//Variables
int acc_error=0; //We use this variable to only calculate once the Acc data error
float rad_to_deg = 180/3.141592654; //This value is for pasing from radians to degrees values
float Acc_rawX, Acc_rawY, Acc_rawZ; //Here we store the raw data read
float Acc_angle_x, Acc_angle_y; //Here we store the angle value obtained with Acc data
float Acc_angle_error_x, Acc_angle_error_y; //Here we store the initial Acc data error
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); //begin the wire comunication
Wire.beginTransmission(0x68); //begin, Send the slave adress (in this case 68)
Wire.write(0x6B); //make the reset (place a 0 into the 6B register)
Wire.write(0x00);
Wire.endTransmission(true); //end the transmission
Wire.beginTransmission(0x68); //Start communication with the address found during search.
Wire.write(0x1C); //We want to write to the ACCEL_CONFIG register
Wire.write(0x10); //Set the register bits as 00010000 (+/- 8g full scale range)
Wire.endTransmission(true);
Serial.begin(9600); //Remember to set this same baud rate to the serial monitor
/*Here we calculate the acc data error before we start the loop
* I make the mean of 200 values, that should be enough*/
if(acc_error==0)
{
for(int a=0; a<200; a++)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(0x68);
Wire.write(0x3B); //Ask for the 0x3B register- correspond to AcX
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(0x68,6,true);
Acc_rawX=(Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read())/4096.0 ; //each value needs two registres
Acc_rawY=(Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read())/4096.0 ;
Acc_rawZ=(Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read())/4096.0 ;
/*---X---*/
Acc_angle_error_x = Acc_angle_error_x + ((atan((Acc_rawY)/sqrt(pow((Acc_rawX),2) + pow((Acc_rawZ),2)))*rad_to_deg));
/*---Y---*/
Acc_angle_error_y = Acc_angle_error_y + ((atan(-1*(Acc_rawX)/sqrt(pow((Acc_rawY),2) + pow((Acc_rawZ),2)))*rad_to_deg));
if(a==199)
{
Acc_angle_error_x = Acc_angle_error_x/200;
Acc_angle_error_y = Acc_angle_error_y/200;
acc_error=1;
}
}
}//end of error calculation
}//end of setup void
void loop() {
//////////////////////////////////////Acc read/////////////////////////////////////
Wire.beginTransmission(0x68); //begin, Send the slave adress (in this case 68)
Wire.write(0x3B); //Ask for the 0x3B register- correspond to AcX
Wire.endTransmission(false); //keep the transmission and next
Wire.requestFrom(0x68,6,true); //We ask for next 6 registers starting withj the 3B
/*We have asked for the 0x3B register. The IMU will send a brust of register.
* The amount of register to read is specify in the requestFrom function.
* In this case we request 6 registers. Each value of acceleration is made out of
* two 8bits registers, low values and high values. For that we request the 6 of them
* and just make then sum of each pair. For that we shift to the left the high values
* register (<<) and make an or (|) operation to add the low values.
If we read the datasheet, for a range of+-8g, we have to divide the raw values by 4096*/
Acc_rawX=(Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read())/4096.0 ; //each value needs two registres
Acc_rawY=(Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read())/4096.0 ;
Acc_rawZ=(Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read())/4096.0 ;
/*Now in order to obtain the Acc angles we use euler formula with acceleration values
after that we substract the error value found before*/
/*---X---*/
Acc_angle_x = (atan((Acc_rawY)/sqrt(pow((Acc_rawX),2) + pow((Acc_rawZ),2)))*rad_to_deg) - Acc_angle_error_x;
/*---Y---*/
Acc_angle_y = (atan(-1*(Acc_rawX)/sqrt(pow((Acc_rawY),2) + pow((Acc_rawZ),2)))*rad_to_deg) - Acc_angle_error_y;
/*Uncoment the rest of the serial prines
* I only print the Y raw acceleration value */
//Serial.print("AccX raw: ");
//Serial.print(Acc_rawX);
//Serial.print(" | ");
//Serial.print("AccY raw: ");
//Serial.print(Acc_rawY);
//Serial.print(" | ");
Serial.print("AccZ raw: ");
Serial.print(Acc_rawZ);
Serial.print(" | ");
//Serial.print("AccX angle: ");
//Serial.print(Acc_angle_x);
//Serial.print(" | ");
Serial.print("AccY angle: ");
Serial.print(Acc_angle_y);
Serial.println(" ");
}
Go back:

 About me
About me  History
History  Let's learn
Let's learn  Contact us
Contact us  Arduino tutorials
Arduino tutorials Circuits tutorials
Circuits tutorials  Robotics tutorials
Robotics tutorials Q&A
Q&A Blog
Blog  Arduino
Arduino  Circuits
Circuits Robotics
Robotics  Modules
Modules  Gadgets
Gadgets  Printers
Printers  Materials
Materials  3D objects
3D objects  3D edit
3D edit  Donate
Donate  Reviews
Reviews  Advertising
Advertising